Alternatives Database
Neuromuscular Pharmacology
Producer: Sheffield BioScience Programs Normal 0 false false false EN-CA X-NONE X-NONE MicrosoftInternetExplorer4 Normal 0 false false false EN-CA X-NONE X-NONE MicrosoftInternetExplorer4 /* Style Definitions */ table.MsoNormalTable {mso-style-name:"Table Normal"; mso-tstyle-rowband-size:0; mso-tstyle-colband-size:0; mso-style-noshow:yes; mso-style-priority:99; mso-style-qformat:yes; mso-style-parent:""; mso-padding-alt:0cm 5.4pt 0cm 5.4pt; mso-para-margin-top:0cm; mso-para-margin-right:0cm; mso-para-margin-bottom:10.0pt; mso-para-margin-left:0cm; line-height:115%; mso-pagination:widow-orphan; font-size:11.0pt; font-family:"Calibri","sans-serif"; mso-ascii-font-family:Calibri; mso-ascii-theme-font:minor-latin; mso-fareast-font-family:"Times New Roman"; mso-fareast-theme-font:minor-fareast; mso-hansi-font-family:Calibri; mso-hansi-theme-font:minor-latin;} /* Style Definitions */ table.MsoNormalTable {mso-style-name:"Table Normal"; mso-tstyle-rowband-size:0; mso-tstyle-colband-size:0; mso-style-noshow:yes; mso-style-priority:99; mso-style-qformat:yes; mso-style-parent:""; mso-padding-alt:0cm 5.4pt 0cm 5.4pt; mso-para-margin-top:0cm; mso-para-margin-right:0cm; mso-para-margin-bottom:10.0pt; mso-para-margin-left:0cm; line-height:115%; mso-pagination:widow-orphan; font-size:11.0pt; font-family:"Calibri","sans-serif"; mso-ascii-font-family:Calibri; mso-ascii-theme-font:minor-latin; mso-fareast-font-family:"Times New Roman"; mso-fareast-theme-font:minor-fareast; mso-hansi-font-family:Calibri; mso-hansi-theme-font:minor-latin;}Normal 0 false false false EN-CA X-NONE X-NONE MicrosoftInternetExplorer4 Normal 0 false false false EN-CA X-NONE X-NONE MicrosoftInternetExplorer4 /* Style Definitions */ table.MsoNormalTable {mso-style-name:"Table Normal"; mso-tstyle-rowband-size:0; mso-tstyle-colband-size:0; mso-style-noshow:yes; mso-style-priority:99; mso-style-qformat:yes; mso-style-parent:""; mso-padding-alt:0cm 5.4pt 0cm 5.4pt; mso-para-margin-top:0cm; mso-para-margin-right:0cm; mso-para-margin-bottom:10.0pt; mso-para-margin-left:0cm; line-height:115%; mso-pagination:widow-orphan; font-size:11.0pt; font-family:"Calibri","sans-serif"; mso-ascii-font-family:Calibri; mso-ascii-theme-font:minor-latin; mso-fareast-font-family:"Times New Roman"; mso-fareast-theme-font:minor-fareast; mso-hansi-font-family:Calibri; mso-hansi-theme-font:minor-latin;} /* Style Definitions */ table.MsoNormalTable {mso-style-name:"Table Normal"; mso-tstyle-rowband-size:0; mso-tstyle-colband-size:0; mso-style-noshow:yes; mso-style-priority:99; mso-style-qformat:yes; mso-style-parent:""; mso-padding-alt:0cm 5.4pt 0cm 5.4pt; mso-para-margin-top:0cm; mso-para-margin-right:0cm; mso-para-margin-bottom:10.0pt; mso-para-margin-left:0cm; line-height:115%; mso-pagination:widow-orphan; font-size:11.0pt; font-family:"Calibri","sans-serif"; mso-ascii-font-family:Calibri; mso-ascii-theme-font:minor-latin; mso-fareast-font-family:"Times New Roman"; mso-fareast-theme-font:minor-fareast; mso-hansi-font-family:Calibri; mso-hansi-theme-font:minor-latin;}
normal">** This item is archived as it is no longer available. It is detailed here for reference purposes only **An interactive, menu driven and easy to use program which simulates experiments performed on the sciatic nerve-anterior tibialis muscle preparation of the cat (in vivo) to illustrate the important differences in the pharmacological action of depolarizing and non-depolarizing blocking agents.
An on-screen student handbook covers:
an outline, using text and graphics of the process of neuromuscular transmission
- the preparation of the anaesthetised cat,
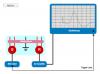
- the protocol for sciatic nerve stimulation and isometric recording of evoked contractions of the anterior tibialis muscle.
- a summary of the actions of the different types of blocking agents
- theclinical relevance of the different blocking agents.
The Experiments Section presents high-resolution graphic simulations of experimental results (muscle contractions), in accelerated time, on a scrolling display to simulate a chart recorder.
Phase I experiments - each experiment compares the action of the two types of neuromuscular blocking agent using d-tubocurarine as an example of a non-depolarizing blocker and decamethonium as an example of a depolarizing blocker.
- administeredi.v.
- administeredclose arterially
- inconjunction with an anticholinesterase
- inconjunction with a different competitive (non-depolarizing)
- blocker
- inconjunction with a different depolarizing blocker
- inresponse to tetanic stimulation
- inresponse to acetylcholine administered by close arterial injection.
Phase II experiments
- the effects of four successive doses of decamethonium followed by the effects of tetanic stimulation and an anticholinesterase
Student Activities
Each experiment has an associated student activity designed to assess understanding of the experimental results. These might be a series of true/false statements or a table to complete.There are also some suggested questions which would form the basis of a report of the experiment.
Language Versions: English
Recommended System Requirements:
Windows:
Microsoft Windows XP (32 bit), Windows Server 2003 (32-bit), Windows Server 2008 (32 bit), Windows Vista (32 bit), Windows 7 (32 bit and 64 bit), Windows 8
2.33GHz or faster x86-compatible processor, or Intel Atom 1.6GHz or faster processor for netbooks 128MB of RAM (1GB of RAM recommended for netbooks); 128MB of graphics memory Internet Explorer 7.0 or later, Mozilla Firefox 4.0 or later, Google Chrome, Safari 5.0 or later, or Opera 11.
Mac OS:
Mac OS X v10.6, v10.7, or v10.8
Intel Core Duo 1.83GHz or faster processor
256MB of RAM; 128MB of graphics memory
Safari 5.0 or later, Mozilla Firefox 4.0 or later, Google Chrome, or Opera 11
Target Audience: Undergraduate pharmacology, medical, bioscience and pharmacy students.
Price: £250 (multiuser, educational license)